In my last blog post, 2021 B2B SEO Planning Guide Part 2: Content Strategy for Higher Rankings, we explored how recent changes to Google have altered the historical landscape for content planning. Specifically, we talked about how rankings are keyword dependent now in terms of what kind of content is most likely to rank on page one of the search results. The same is also true for what search features are displayed. In this post, we will look at how recent changes (and even historical ones) have dramatically shifted the conversation around keyword rankings and what opportunities exist to achieve rankings, or have content displayed on page one outside of the traditional 10 blue links that used to be the sole focus of search results.
While I'll dive into Universal Search and other search enhancements later in this series, the scope of this post will be to understand the opportunities that exist around Universal search in the beginning of 2021, as well as some general strategic concepts that are specific to B2B that will allow you to maximize your ability to take advantage of these opportunities.
Definition of Universal Search
Let's start by setting some baseline definitions that will be useful for those unfamiliar with some of the topics we are going to discuss. This article from MOZ sets a good starting foundation for the term SERP feature and defines some of the most common features including Universal Search:
What is a SERP feature?
A SERP feature is any result on a Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) that is not a traditional organic result. The most common SERP Features are:
- Rich Snippets which add a visual layer to an existing result (e.g., review stars for product ratings)
- Universal Results that appear in addition to organic results (e.g., image results, new results, featured snippets)
- Knowledge Graph data which appears as panels or boxes (e.g., weather, Celebrity Knowledge Panel)
- Paid Results that are bought by bidding on keywords (e.g., AdWords or Google Shopping)
In the early days of Google, every result on the SERP looked the same.
We'll cover the first three search features listed above here. And, for our purposes, we will consider the Knowledge Graph a potential Universal Search Result to keep things simple.
The difference between Search Enhancements and Universal Search results can be a little fuzzy, and for the most part the distinction isn't all that important from the standpoint that you want to target both sets of Search Features in your optimization strategy. In fact, many people (as well as Google) use these terms interchangeably. For the sake of consistency, we will refer to enhancements as search features that add additional information to one of the traditional blue links found in search results. We will define Universal Search results as additional results or entities that live outside of the blue links but that can still show up in search results or that have their own searchable database (for example, video search, image search, book search, or maps).
For example, a video can be featured in a video carousel which is a Universal Search result, or it can be featured as a thumbnail for the page that it is embedded on, where it would be a Search Enhancement.
Here is a video carousel that ranks for the phrase 'Universal Search' which features three videos and links to others:
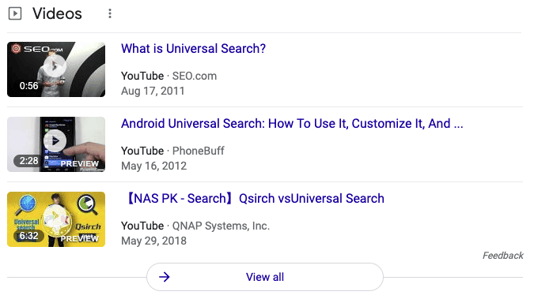
And here is a listing for SEO.com with a video thumbnail (Search Enhancement) that augments their regular listing in search results:

Our definitions of Universal Search and Search Enhancements help us differentiate these search features that are both specific to video. This distinction will help us differentiate which tactics augment your search results and which tactics can get you inclusion into other stand alone results that are not the regular blue links. It also helps to better understand the potential results for any given content type, schema implementation, or optimization tactic.
History of Universal Search
Universal search was officially born in Google on May 16th, 2007. Universal Search was a fundamental shift in search, search technology, and user expectations of what search could and should provide.
A lot has changed over the years to bring us to where we are today with the huge, keyword specific diversity that exists between search engine results. In the next section of this post, we will begin to identify all of these opportunities and figure out which ones are the most important for B2B companies that want to attract potential customers.
Types of Search Features
Google doesn't necessarily differentiate between Universal Search Results and Enhancements in the same way we do for this discussion. They differentiate search features as follows:
Google Search results include many types of display features. How they look changes over time, and the same result can be displayed differently depending on whether you're seeing it on a desktop computer or a phone, what country you are in, or many other factors. Google is trying to show a result in the most useful format for the searcher. These search results mostly fall into the following general categories:
Plain blue link |
The beloved, the original. The term "plain blue link" is not an official term, but is commonly used outside of our official documentation. Results typically contain Title, URL and Snippet. |
Enhancement |
You can enhance your plain or rich results with several types of enhancements, including breadcrumbs, sitelinks search boxes, corporate logos, and more. Most enhancements require structured data on the page. *note: this is mostly consistent with our definition but Google includes corporate logos that appear in Knowledge panels meaning their definition of enhancements is not as limited as the one we are using. |
Rich result |
A rich result is a result that contains graphical elements, including review stars, thumbnail images, or some kind of visual enhancement. Rich results can stand alone in search results, while some types of rich result can be included in a carousel of results. The exact appearance can change over time as Google refines the optimal layout and behavior of a result type. Rich results with a more immersive experience are called enriched results and feature advanced interaction capabilities. It should be noted that Google also considers Search Features like FAQ, Reviews, and Images as rich results which are enhancements by our definition. So not all Rich Results are Universal Search results based on our definition. |
Knowledge panel entry |
The Google knowledge panel is a collection of information from one or more pages, displayed in a rich result with images, text, and links. It can be difficult to distinguish visually between a rich card and a knowledge panel result. Knowledge panel results can include identity (logo, preferred site name). The knowledge panel can potentially ingest data using any schema.org elements, even those not described in this documentation. We will consider Knowledge Panels and Rich cards to be Universal Search Results. |
Featured snippet |
When a user asks a question in Google Search, we might show a search result extracted from your site in a special featured snippet block at the top of the search results page. We will consider Featured Snippets to be Universal Search Results. |
OneBox result |
A OneBox result presents an inline answer or a tool in search results. Examples include the local time OneBox or the translation OneBox. You can't add a custom OneBox to search results. We will consider OneBox results. |
Discover |
Not part of Google Search results, but your page can appear in a scrolling list of results shown in a special viewing panel on Android devices. Each result card summarizes a single page. We will consider any Discover results as part of Universal Search because they do not enhance the 10 traditional blue links and live in a different database. |
|
Reference: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/appearance/search-result-features |
|
Within these segments, there are a huge number of potential search features that can occur based on the keyword that is used in search.
seoClarity just released a report in December 2020 that detailed their analysis of 6.3 million keywords and found over 1200 potential variations to search features.
Admittedly this report included very small variances, but it was an increase of more than 400 variations from the same analysis the previous year. There were only 200 of these variations found on more than .2% of keywords, meaning that the vast majority of keywords have a much smaller pool of potential features and differences. At the same time, the data indicates that the number of potential opportunities that need to be identified and monitored continues to expand. Additionally, more attention will be required on a per keyword basis to optimize for them. The takeaway: you should manually review what search features exist across your target keywords and develop a plan for optimizing for those features as part of your SEO strategy.
Search Features and Schema
There are a number of possible search features. Some of these features require Schema.org structured data for eligibility. In other cases, structured data is not a requirement but can ensure that Google understands your content in the right context to make it eligible, or give you more control of how Google displays your content (Breadcrumb is a good example of this). Though, do keep in mind that schema is not a guarantee of inclusion nor does it help rankings.
The following list details the enhancements that require or are aided by schema (note: this list is subject to change as Google adds more features):
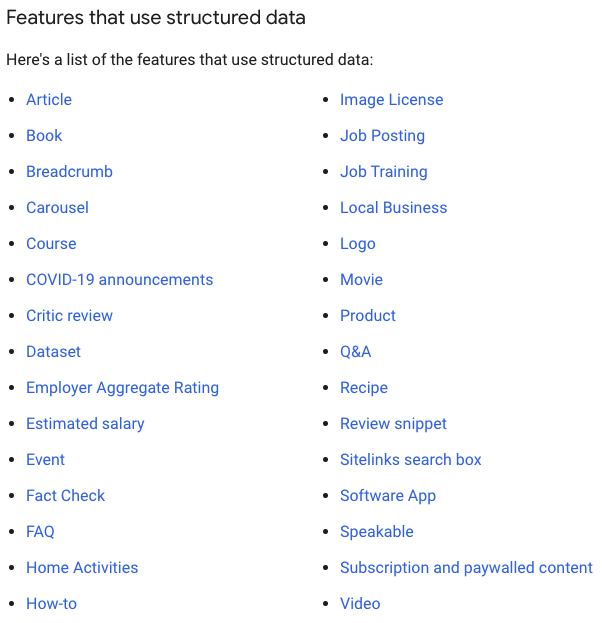
Reference: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/appearance/overview
The search gallery page is a quick reference on how each of these content types might appear in search.
Each of these content types also have another page that contains more examples and detailed implementation requirements, starting with the Article page (the other content types can be found in the left hand navigation of this page).
Furthermore, there is another subset of these content types that Google refers to as Enriched Results that do require schema implementation for eligibility.
The appearance of these results and their functionality depend on the data type as per the following quote from the Enriched Search Results page:
Some rich result types are only available as enriched search types (for example, recipes, jobs, and events); other rich result types can be extended to be an enriched search type with the addition of a few properties. The documentation for a rich result type should say whether and how it can be extended from a basic rich result to an enriched result.
For a B2B website, you'll find that the five most common types of schema search enhancements are:
- Organization
- FAQ
- Review
- Video
- Event
Organization
Organization schema markup creates brand signals which help Google understand who you are without ambiguity. It is recommended to have Organization schema on one page of your site even though it is not featured in the Google search enhancements gallery. These signals can enhance your Knowledge Graph card in the SERPs.
FAQ
FAQ schema makes it easier for Google to understand your content and how it might relate to featured snippets. Google can also generate FAQ Questions and Answers in search listings. For example, when searching erp system, you'll see FAQ such as "What are Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems?" and more. This additional screen real estate and potential engagement is likely to significantly increase CTR for this listing. I highly recommend definitional FAQ content being a part of your B2B SEO Content Strategy.

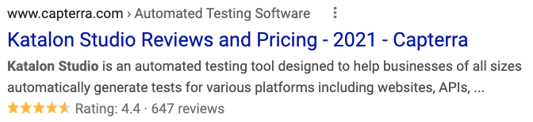
Review
Reviews schema can exist in a number of different contexts especially for products, software applications or companies. Currently, the following enhancement is shown for the term 'Katalon Studio', providing additional screen real estate with the potential to drive interest
In addition to Reviews being implemented within Product schema, they can also be implemented in Organization schema or Local Business schema at the company level.
Video
Video schema helps videos show up in carousels and can generate video thumbnail images in search results which increase CTR. In addition, your videos can appear in Google video search results as well as Google Discover. Implementing schema markup on all video content should be a standard practice for all Web sites.
Video Thumbnail Example for 'cybersecurity and crime':
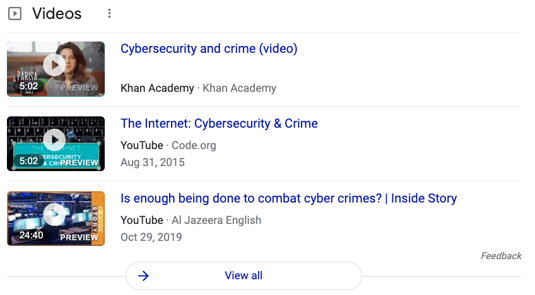
Carousel example for 'cybersecurity and crime': Notice Khan Academy is the only link in the initial results that does not point to YouTube.
Event
Marking up your events with schema can temporarily increase your search listing real estate. For instance, when searching 'marketing conferences', the following listings currently appear:

B2B Universal Search and Search Enhancement Opportunities
As mentioned, not all search features require schema and, at times, your content may be used in search features without schema markup implemented on your site. In some cases, additional data sets beyond schema are used to power some search features. Most notable is your local business listing, your Knowledge Panel for your company, and your products found in Shopping results. Google uses your brand account (which is separate from your Google Business listing), your Google Places account, your Google shopping feed data, and various other data sources to generate these search features as well as others.
In certain instances, Google will just use the content on your site even if it does not have schema markup. This is especially true for Featured Snippets based on lists or definitions. This is an instance where, though not required, schema does make it easier for Google to understand your content in the appropriate context, which obviously makes it more eligible.
As you look for opportunities to extend your B2B targeted footprint across Google search and other surfaces, here are some of the most important search features that I would recommend targeting and optimizing for in 2021:
Priority B2B Search Features
Universal Search Result |
Schema Type |
Other Database |
| Knowledge Panel | Organization* | Google Brand Account |
| Google Brand Account | FAQ, How To, Video, Q&A, Image** | |
| Google Maps Listing | Local Business | Google Maps, Google MyBusiness |
| Local Pack / Local Teaser Pack | Local Business | Google Maps, Google MyBusiness |
| PAA Listing | FAQ | |
| Video Carousel Inclusion | Video | |
| Image Carousel Inclusion | Depends on the Context of the Image | |
| Product Listings | Product | Google Shopping Feed |
| Product Info in Google Images | Product | |
| Twitter Pack | None | |
| Top Stories | Article / BlogPosting + AMP | Google Publisher Center |
| News Listings / News Carousel | Article / BlogPosting + AMP | Google Publisher Center |
| Event Carousel | Event | |
| Logo Image / Knowledge Panel | Logo | |
| Job Posting | Job Posting | |
| Sitelinks | None | |
| Search Box | Search Box | |
| FAQ | FAQ | |
| Price / Shipping / Availability | Product | |
| Ratings / Reviews | Review / Rating + Product / Local Business / Event / Software App *** | |
| Video Thumbnail | Video | |
| Breadcrumb | Breadcrumb | |
| Article Enhancements | Article / BlogPosting | |
| Software App In Mobile | Software App | |
| Image License | Image License |
* Note about Organization: Though no example in Google Feature Guides for Organization schema, I've linked to a valid article from SEMRush (last updated 12/11/2020).
** Note about Images:
